We need to know and understand the process of booting a Cisco Router in the network. This information is vital, especially for us network administrators and IT professionals. Also, if we know the stages of the boot process, we can solve problems better and efficiently.
In this article, I will clarify the stages of the boot process step by step. In short, the first stage is the POST test. After that, the routing device finds and loads the IOS. Then, the configuration file comes into play and loads the settings. Let’s literally get started and explore the details!

How to Boot a Cisco Router?
The boot process of a Router is like the hardware test or POST process done on computers. The operation or opening mode of the Cisco Router occurs in 3 stages.
These stages occur quickly, and the device opens. If there is any problem during the opening, it will give an error, and the routing device will not open. Or it will enter Setup Mode when it cannot find the initial file.

Step 1: Router POST Testing and Bootstrap Initialization
When the Router is powered on, the first thing that happens is to start the POST and Bootstrap.
First, the POST process will start, and the device hardware will be tested. If it finds no errors, it will load Bootstrap.
Step 2: Locate and Load IOS During Boot
In the second step, the Cisco Router runs Bootstrap and searches for the location of the IOS, finds it, and loads it into RAM.
It first searches for the IOS software in its Flash memory. If it cannot find it there, it searches for a TFTP server in the network environment, and if it finds it, it tries to load the IOS. If it connects to the TFTP and still cannot find the IOS, it loads the initial config file.
By default, it loads the IOS software from its own Flash Disk. You can configure another location as default instead of the Flash Disk.
Step 3: Locate and Run the Startup Configuration File
After the second step, after the Router has loaded the IOS software, Bootstrap looks for a startup-config file in NVRAM. If it does not find such a file, it enters setup mode to create a new startup file.
If the bootloader finds this file, it copies it directly to RAM.
The startup config file contains all the settings previously made on the Cisco device. These configurations include all the settings, such as Interface configurations, routing information, and Console passwords.
What Settings Does a Cisco Router’s Initial Configuration File Contain?
The initial config file of a Cisco network equipment contains all the previous settings. That is, these are interface configurations, routing information, and console password. In addition, security and access control setups are also available.
- Interface Configurations
The first file contains the configurations of all interfaces. It also includes things such as IP addresses, subnet masks, descriptions, etc.
- Routing Information
Static routes and dynamic routing protocols are included in the file. Additionally, other routing-related information, such as route maps and ACLs, are also available.
- Console Password
The password you set for your Router’s console port is also in this file. That is, the password provides authorized access to the management console.
- Security and Access Control Configs
This file contains ACLs, firewall rules, and VPN setups. In short, security configurations help control network traffic and ensure security.
- DHCP and NAT Configurations
If the routing device includes DHCP services or NAT configurations, they are also included in the file.
- Quality of Service (QoS)
QoS policies, traffic shaping, and prioritization are in this file. If you have these things, you will optimize your network traffic.
- SNMP and Management
The file contains SNMP configurations that allow it to be monitored, as well as other administrative settings.
- Time and Date
The file contains the time synchronization, time zone, and daylight saving time customizations.
As a result, the initial config file collects the equipment settings. Then, using this information, the Cisco equipment powers itself.
What is a Startup-Config File?
The Startup-Config file is a config file that is kept in RAM (NVRAM). Even if the Cisco equipment is turned off, the startup configuration file is not deleted from NVRAM.
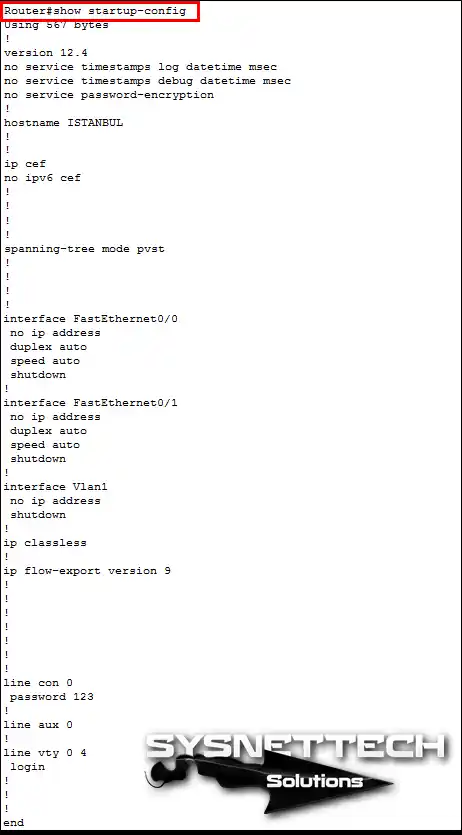
What is a Running-Config File?
When the Router is first started, the startup-config file is loaded because no configuration has been made on it. However, when you save all the configurations you have made after configuring the device, these settings are saved in the running-config file.
When you turn the equipment off and on, the running-config file will now be loaded into NVRAM.
For example, you forgot the password for a user account you created on the device. In this case, you can change the configuration file to startup-config to reset the password. In this way, you can start your equipment with the initial configuration settings.
Let’s say you did not save all the changes you made to your equipment for running-config. At this point, when you restart your device, all your settings will be lost.

Saving Settings & Configurations Made on the Router
After you have configured your Cisco Router for your network, you need to save all the settings. You can do this simply by running the copy running-config startup-config command in privileged mode.
Routing Device Working Logic
The uptime of a Cisco device consists of four phases;
- POST Testing and Bootstrap Initialization
- Locating and Loading the IOS
- Locating and Running the Startup Configuration File
- Router Setup Mode

What Information Does the Show Version Command Display?
- IOS Version
- Boot Version
- IOS File
- CPU and Model
- RAM Size
- Number and Types of Interfaces
- NVRAM Size
- Flash Size
- Configuration Record

What Happens If a Cisco Router Encounters an Error During Boot and Post-Testing Phase?
The Cisco device may receive an error during the POST test and boot phase. In this case, the Router cannot proceed to the next steps of the boot process.
Also, the Power On Self Test (POST) checks for hardware problems. If the POST process detects a problem during the test, the Router stops. As a result, it gives an error message or diagnostic information. This information shows you which hardware is causing the problem.
In such cases, we need to fix the hardware error first. By hardware error, I mean it can be in the interfaces, modules, or memory. In other words, we need to replace these broken or faulty parts.
Afterward, when we have solved the problem, we need to power on our Router again. At this stage, if our device passes the POST test, the boot continues. Then, it finds and loads the IOS software. And finally, it runs the initial config file.
How to Boot a Cisco Router? ⇒ Video
Get a deeper understanding of Cisco bootstrap logic by watching our informative video. Don’t forget to join our YouTube channel for more valuable insights!
Conclusion
As a result, the Cisco Router boot order, or stages, do not change. This method is the same in both new and old versions. If you work with network equipment, you need to know these.
Also, if we understand the intricacies of the boot sequence, we make it easier to manage. For example, IT professionals can better manage Routers and solve problems.