This article will show you step-by-step instructions on how to set up and use the GNS3 network simulator software in Ubuntu. This handy tool helps you set up Router or Switch network devices easily. It’s beneficial for those getting ready for Cisco exams to enhance their professional preparation.
We’ll concentrate on using GNS3 with the Ubuntu 24.04 OS Version or newer. Follow our easy steps for a smooth experience. This guide will help you understand a lot, giving you the skills and knowledge to do well in the competitive field of networking.
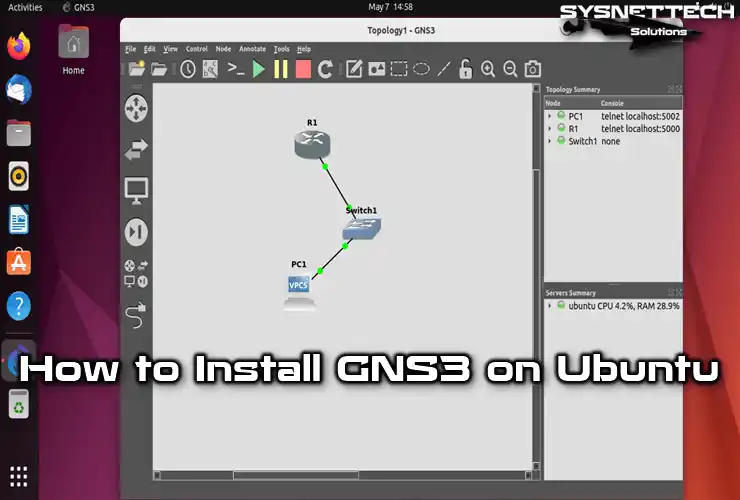
How to Run GNS3 2.2 Versions on Ubuntu 24.04, 23.10, or Newer
You can install the GNS3 networking app on Windows or download, install, and use it on Linux systems without any trouble.
With the GNS3 (Graphical Network Simulator 3), you can make unique network setups and run these devices virtually on your computer. You don’t have to buy network products like Cisco Routers and Switches.
GNS3 is more detailed than the Cisco Packet Tracer program. That’s why people who want to create more advanced network designs like using this simulator program.
On Ubuntu, we typically install applications using the terminal. In Linux, once you add a program’s address, you can install it and automatically get the latest version when you update your system.
However, sometimes, when installing a program on the latest Linux versions, you might need to install some other necessary stuff first. You’ll have to install these extra things for the program to work.
How to Set Up GNS3
Follow the steps below to run the Cisco simulator software on your Linux/Ubuntu distribution without any problems.
Step 1
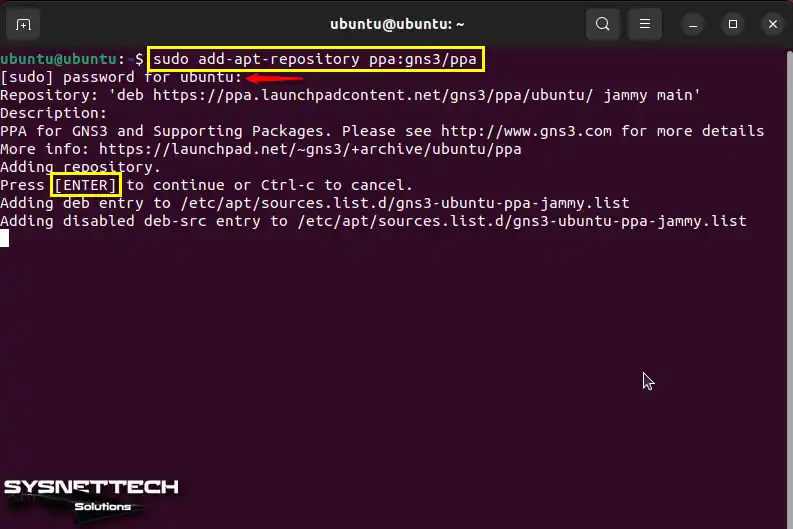
On the Ubuntu desktop, Open Terminal by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T together. To add GNS3 to the Repository, type the following command in the terminal area and press Enter.
To add the GNS3 software’s repo address, enter your system’s root password and press the Enter key. As you can see in the terminal, to cancel this process, press the Ctrl + C keys together.
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gns3/ppaAfter executing the relevant command, type the sudo apt-get update command and press Enter to check the current versions of the programs installed on your Ubuntu system.
Once you check the versions of the installed programs, type in ‘apt list –upgradable’ to see which programs will get an upgrade. If you’re ready to update right away, use ‘sudo apt upgrade.’
NOTE 1: Some services running in the background during the update are blocking the process. In the terminal, you can stop processes causing issues by using the command “sudo kill -9 (Process ID)” and providing the ID numbers of those conflicting services.
NOTE 2: If you get the “dpkg was interrupted” error when you execute the sudo apt upgrade command again, run the “sudo dpkg –configure -a” command, and then you can start the update again.
Step 2
To install the GNS3 simulator, define the repo address, update programs, and run “sudo apt install gns3-server gns3-gui” in the terminal.
sudo apt install gns3-gui gns3-server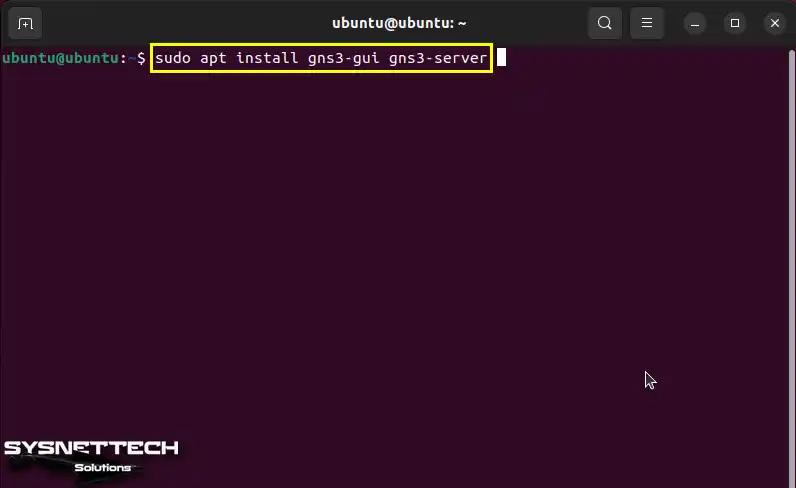
Step 3
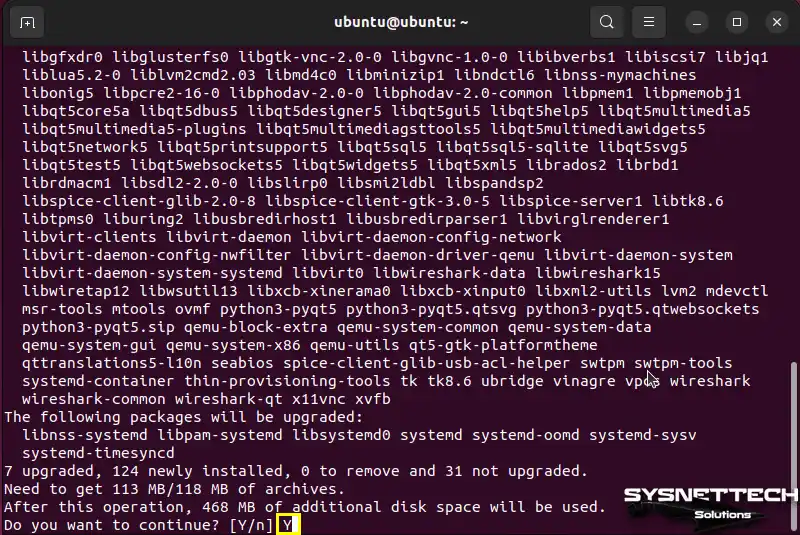
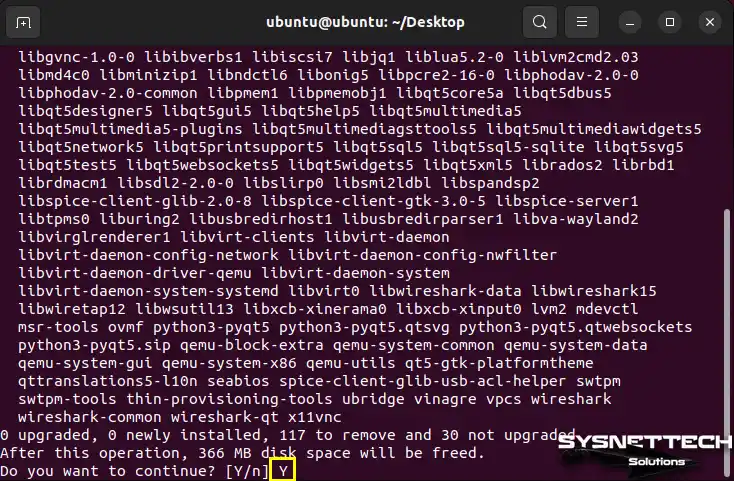
To ensure the simulator program runs smoothly on Ubuntu, we need to install some extra packages. In the terminal, press Y and Enter to say “yes” to installing these special packages.
Make sure you’re connected to the internet so that GNS3 can download the packages it needs.
Step 4
In the final part of the installation, you’ll put in the Wireshark program. But before that, a window for setting up ubridge will pop up.
This screen is about permitting regular group members. Just hit Enter on Yes so that those folks can use i

Step 5
If you want users to be able to check data with Wireshark, just hit Enter to say Yes.

Step 6
After completing the installation, run GNS3 from the applications panel.
Step 7
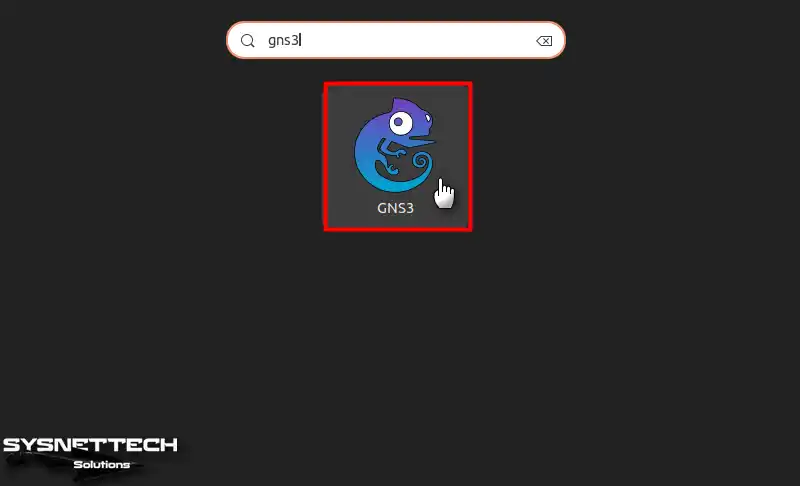
After running the GNS3 simulator, the Setup Wizard window will appear. You can shut down this window or keep going to check and make sure everything is set up right for localhost.
Choose “Run appliances on my computer” and click Next in the Setup Wizard.
Step 8
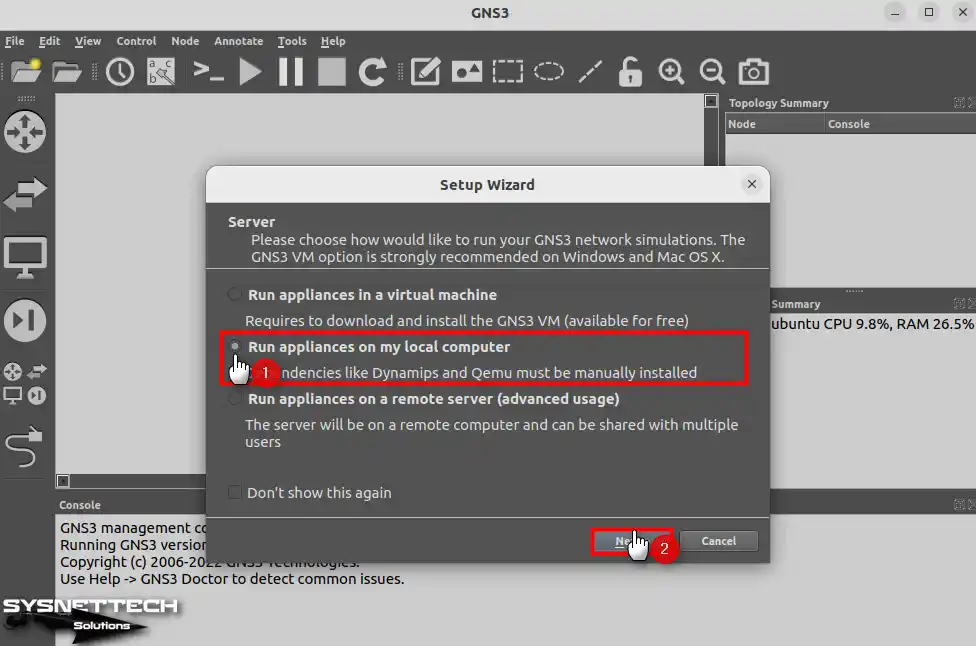
You can continue without changing the default settings in the Local server configuration window. However, if another application on your system may conflict with GNS3, you should change the Port number.
Step 9
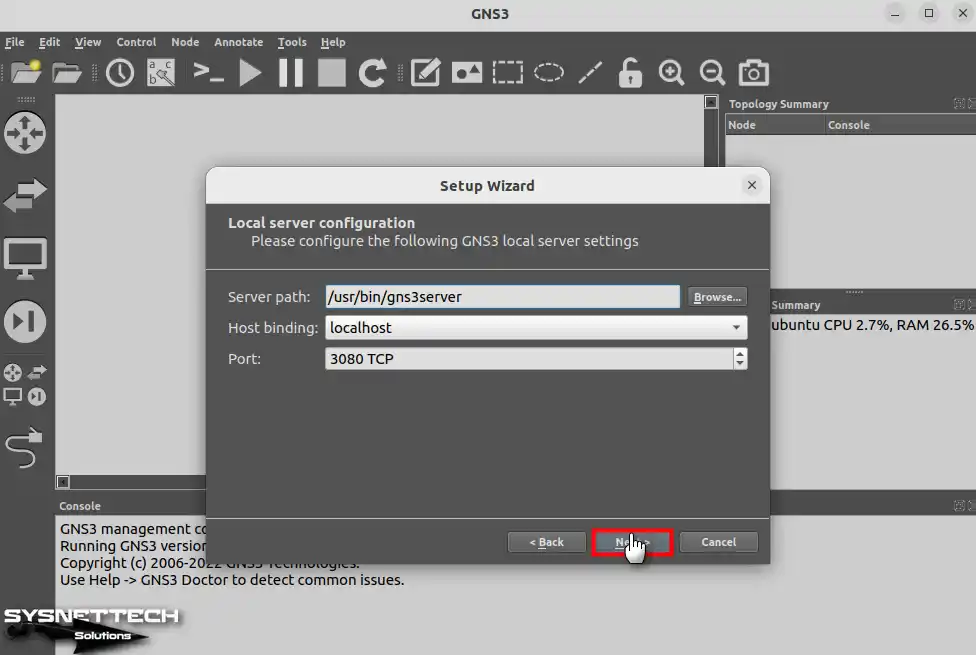
The Localhost service’s status is displayed in the local server status window. It doesn’t conflict with other apps, ensuring smooth operation. In the service verification window, click Next to continue.
Step 10
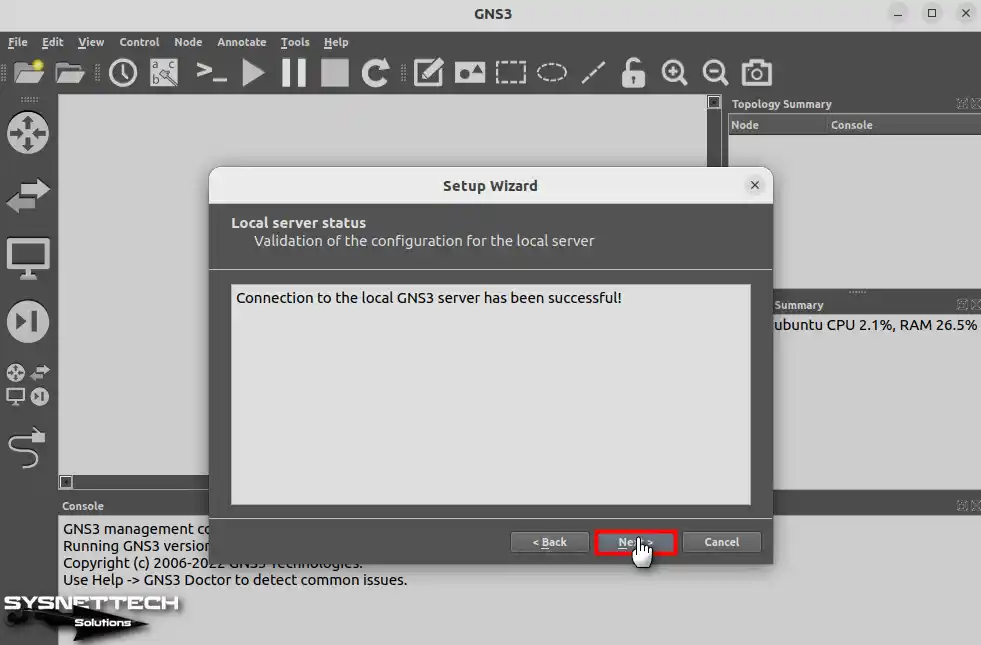
The Summary window shows that the GNS3 simulator software is running locally. Click Finish to close this window and proceed to the next step.

How to Add a Cisco Router
After installing GNS3 on your Ubuntu system, you must add IOS. Therefore, download the Router or switch network systems from our website. You can then add these files to the virtual network software and start using it.
Step 1
You need to add Router IOS to the Cisco simulator and test it. For new IOS, go to File/Preferences in the program’s menu.

Step 2
Open the IOS Router Template: Dynamips/IOS Router > New. Then, click Browse to specify the IOS location for the image section.
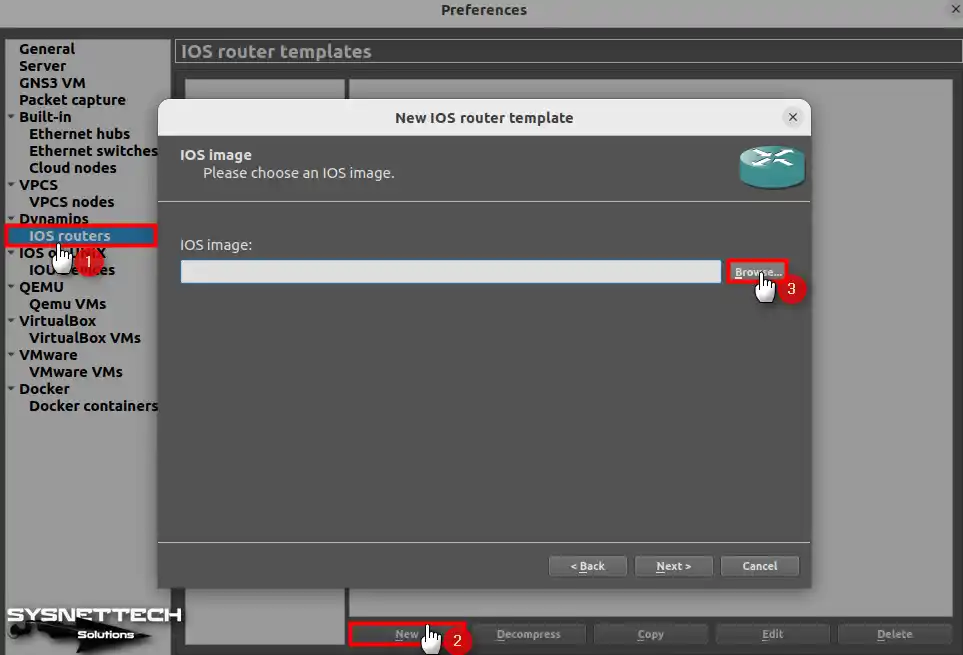
Step 3
Choose “c7200-adventerprisek9-mz.152-4.M7.bin” from the downloaded location on your system. Then, click “Open” to add the iOS image.
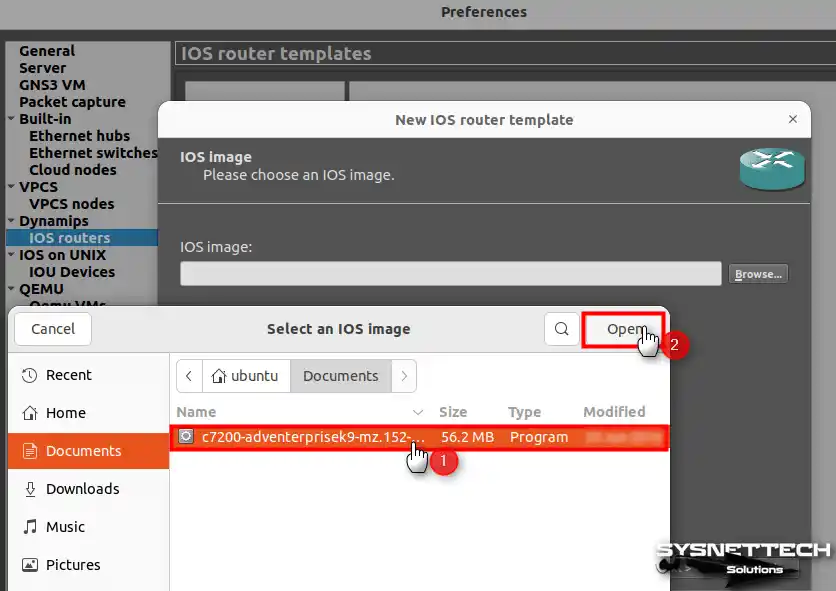
Step 4
Click Yes in the “Would you like to decompress this IOS image” window and continue.

Step 5
After selecting the Router 7200 image, click Next.

Step 6
After adding the device, modify the name and configure the platform type in the Name and Platform window. Then, leave the settings as default and click Next.

Step 7
In the Memory window, you can change the amount of memory for the Router. If you have a powerful computer, you can add a bit more memory to make it work better.

Step 8
In the Network Adapters section, insert a FastEthernet, GigabitEthernet, or Serial Interface into the Router slots. Alternatively, you can use the default C7200-IO-FE (FastEthernet) card.

Step 9
In the Idle-PC window, click the Idle-PC Finder button to set a value automatically. So, it prevents the Router or Switch network devices from using 100% of your CPU.
Let’s say you received the following error while determining the idle-PC value: Turn off GNS3 first, then proceed to the next step.
NOTE: The error mentioned above is due to Dynamips’ incompatibility with GNS3 software on Ubuntu 64-bit.
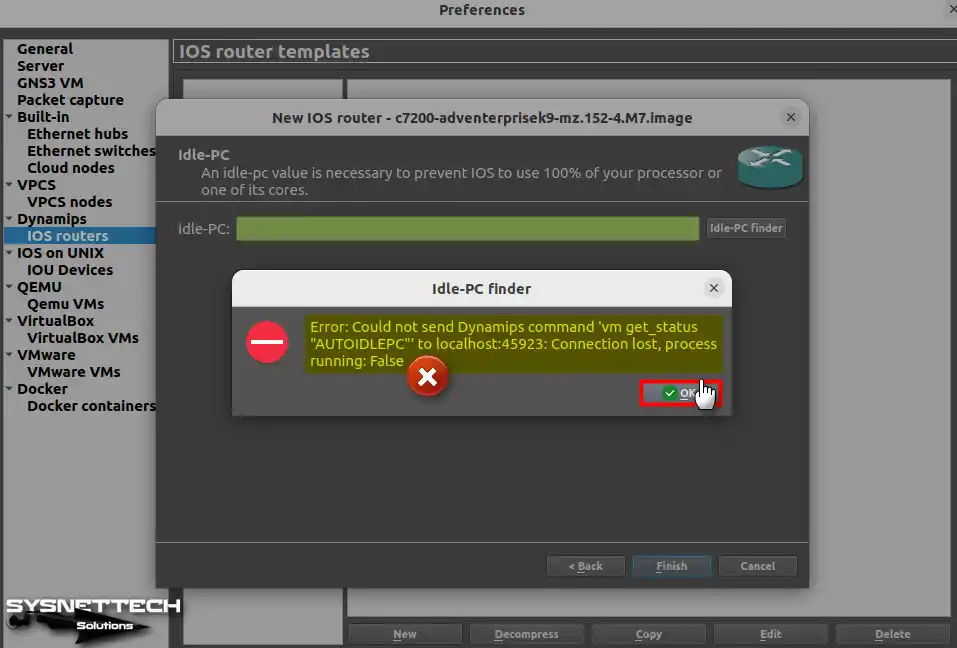
Step 10
To fix the Ubuntu Dynamips error, first open the terminal. Next, run the command “sudo dpkg –add-architecture i386”. When you use this command, you will enable 32-bit architecture on your system.
sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386You enabled 32-bit architecture to resolve GNS3’s 64-bit architecture incompatibility. Now, download and install the Dynamips i386 package with the commands below.
wget http://ppa.launchpad.net/gns3/ppa/ubuntu/pool/main/d/dynamips/dynamips_0.2.21-1~eoan1_i386.deb
sudo dpkg -i dynamips_0.2.21-1~eoan1_i386.deb
Step 11
You might see an error when getting the Dynamips i386 package. To fix it, you need to install the libc6, libelf1, and libpcap0.8 packages.
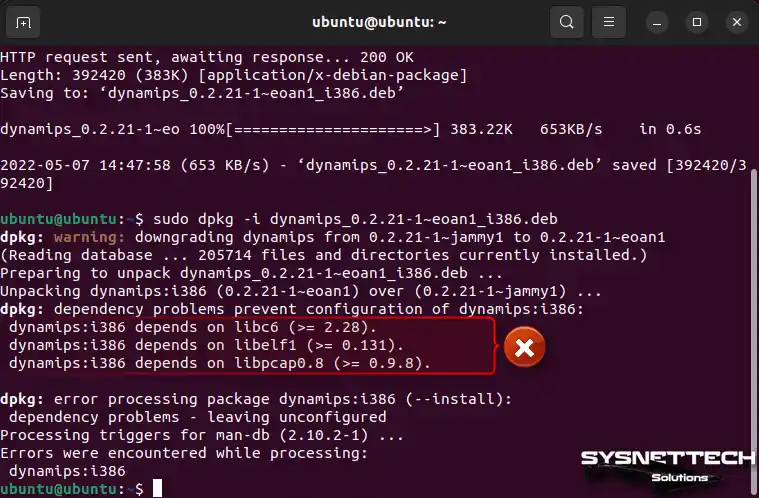
Step 12
To ensure a smooth install, you need to get the packages the deb package needs. To do this, type “sudo apt install—f” in the terminal.
sudo apt install -f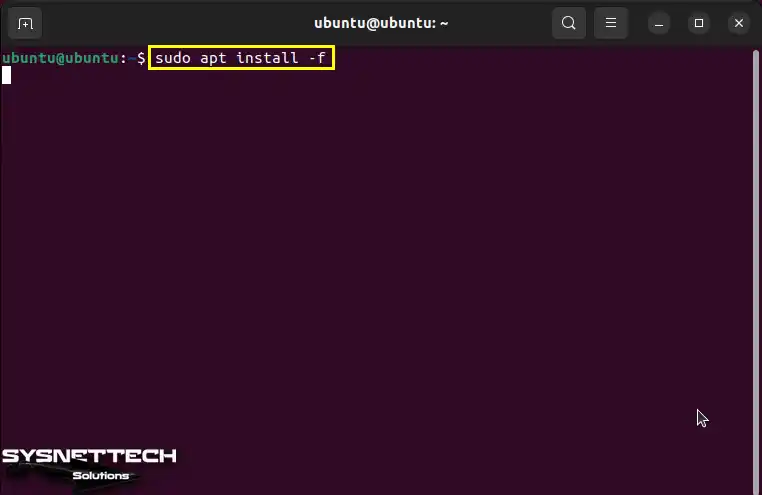
Step 13
You’ll be getting the additional packages, which are about 30 MB in size. Press Y and Enter to say okay and make it happen.
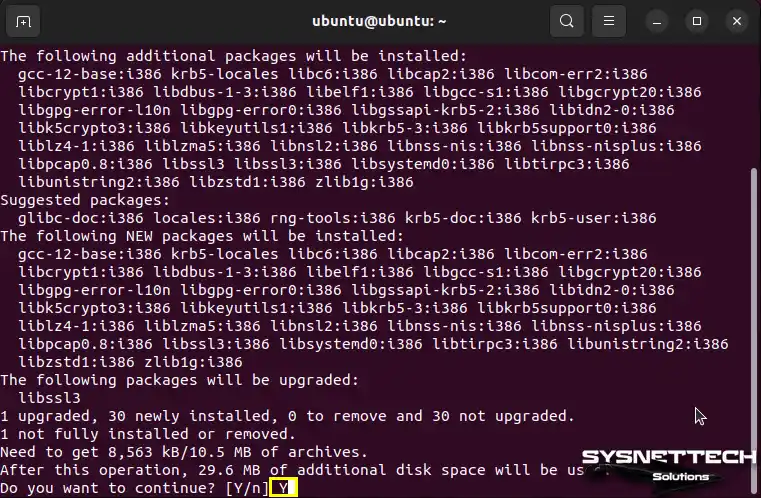
Step 14
After successfully installing the Dynamips 32bit package, open the GNS3 program again and go to the Idle-PC window in the IOS add wizard.
When you press the Idle-PC Finder button to select the correct value for iOS, you will notice that you have solved the error this time.
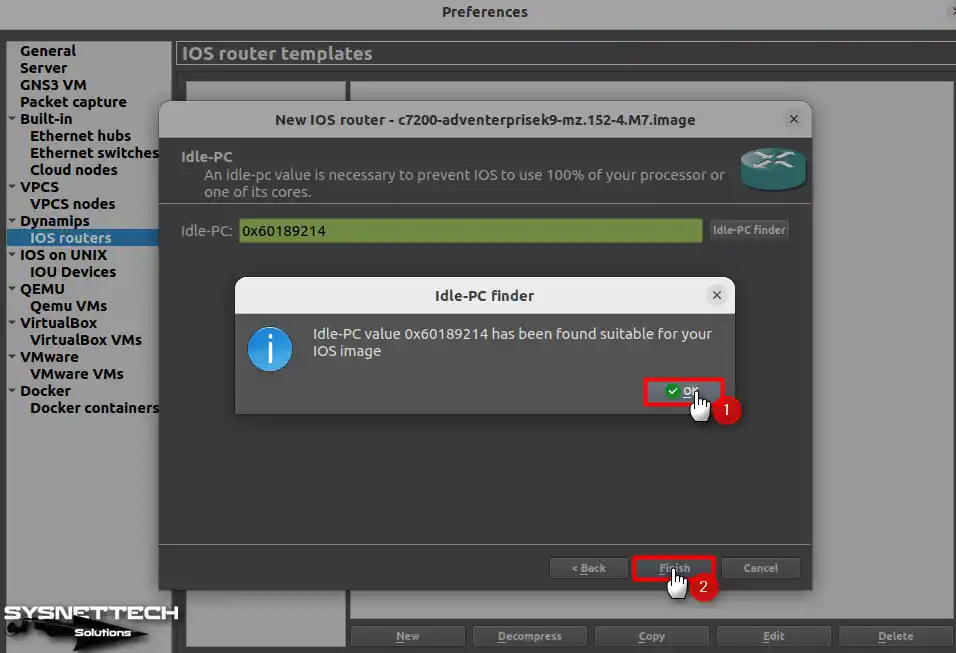
Step 15
After adding the c7200 Router IOS, close the wizard.
How to Create a New Project
You can now form a new project on your Ubuntu system using the Cisco simulator software and start network design.
Step 1
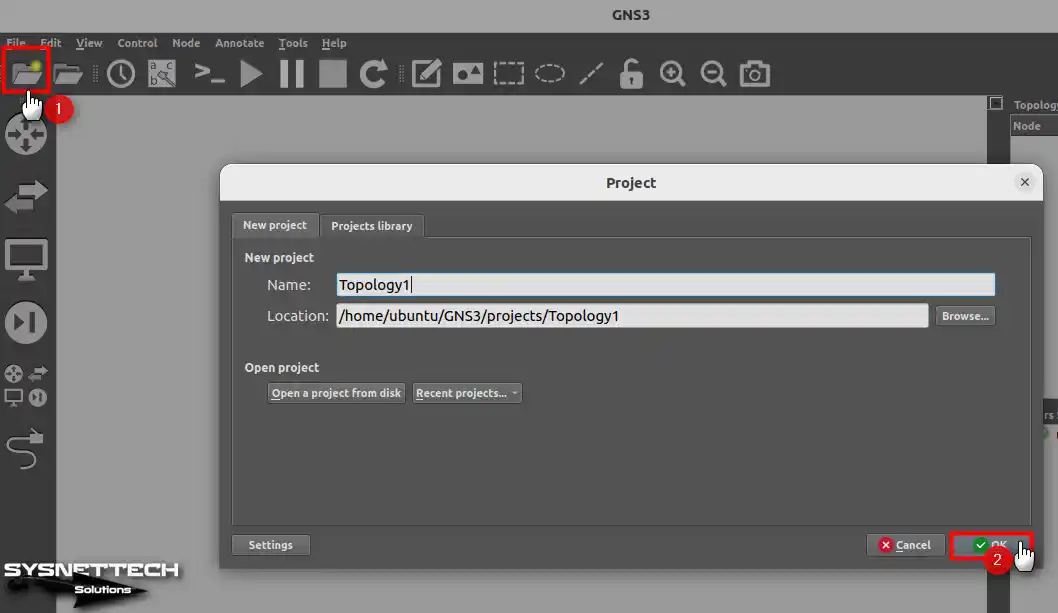
Click on the New Project icon from the GNS3 tool menu, type a name for the network topology in the opened Project window, and click OK after specifying the location to save.
Step 2
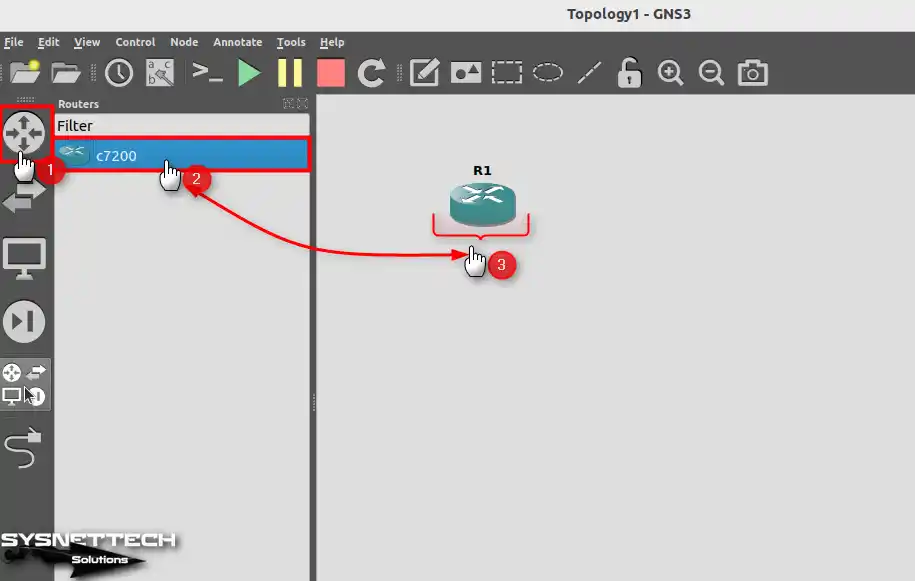
Drag and drop the Cisco Router c7200 that you added to the simulator program to the workspace.
Step 3
Likewise, drag and drop a Cisco Switch and VPCS to the workspace.

Step 4
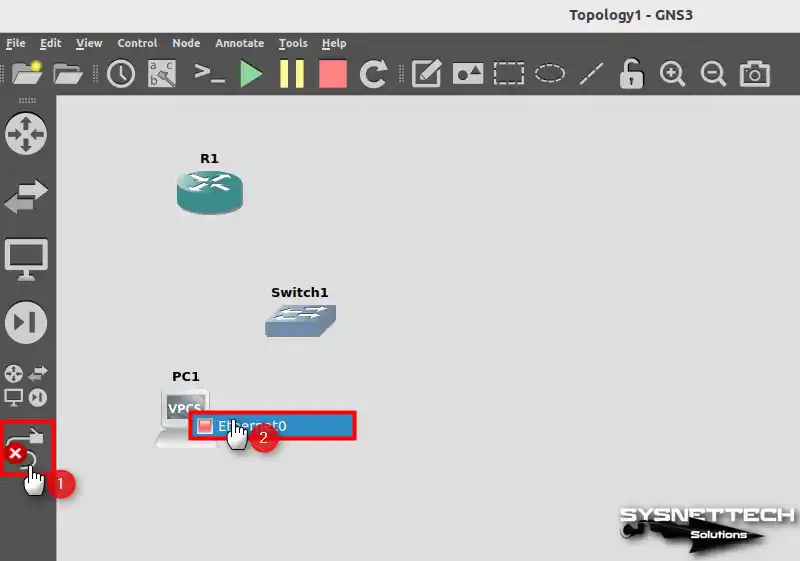
Turn on the cabling option on the left side, then click VPCS and connect one end of the network cable to the Ethernet0 interface.
Step 5
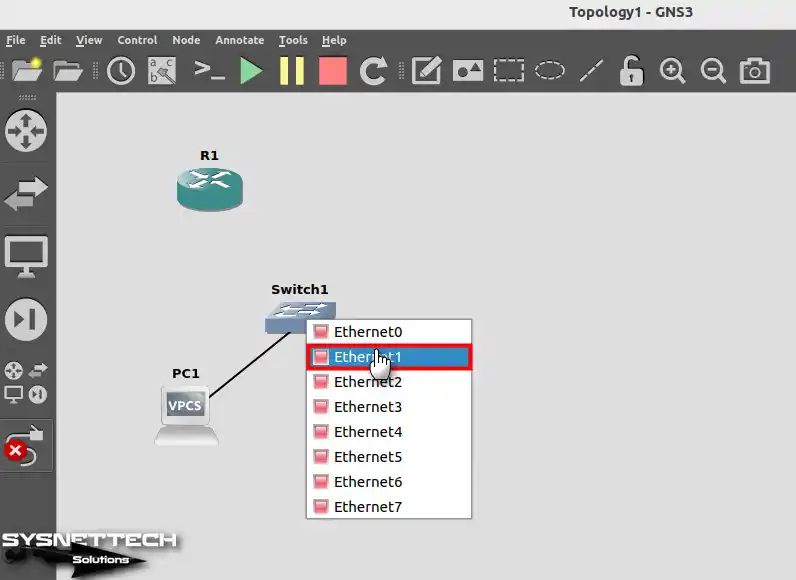
Connect the other end of the cable you connected to the VPCS to the Ethernet1 interface of the Switch.
Step 6
After clicking Router, connect one end of the cable to one of the switch’s accessible interfaces and the other end to the FastEthernet0/0 interface.
In this step, you may encounter a UBRIDGE ERROR while connecting the network cable from the Switch to the Router. To resolve this uBridge error, execute the commands below in the order in the terminal.
sudo apt install git
sudo apt install make
sudo apt install gcc
sudo apt install libpcap-dev
cd ~/Downloads
git clone https://github.com/GNS3/ubridge.git
cd ubridge
make
sudo make install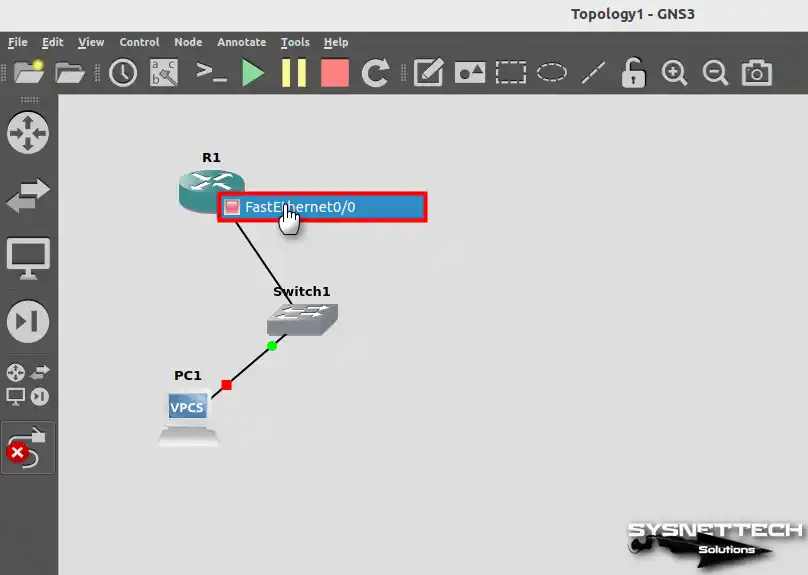
Step 7
To run all the devices in the workspace, click the green arrow on the tool menu and then click Yes to confirm the process of all devices in the window that opens.
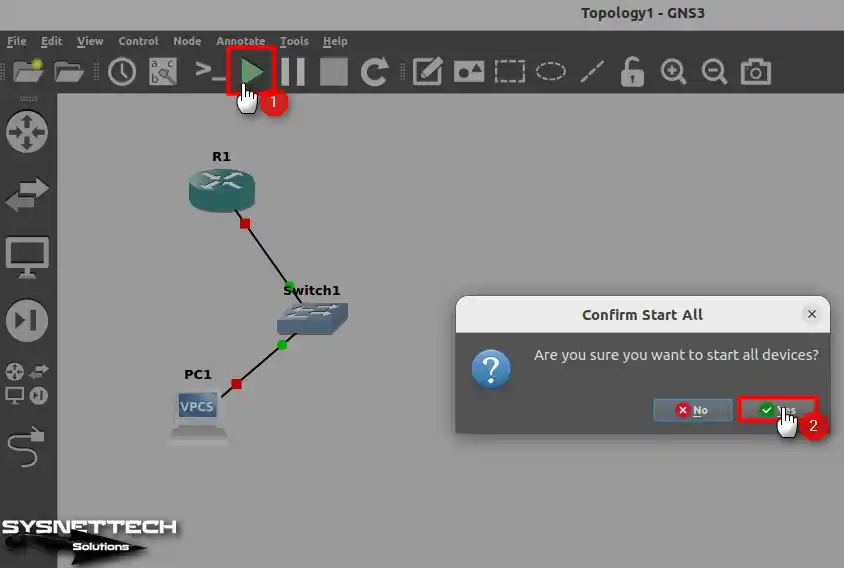
Step 8
After running all devices, double-click on VPCS to open the console. Execute the ip 192.168.1.200/24 in the console to set an IP address to the PC.
ip 192.168.1.200/24
Step 9
Type in the commands below to give an IP address to the FastEthernet0/0 interface of Router R1.
R1# conf t
R1(config)# interface fastethernet0/0
R1(config)# ip address 192.168.1.100 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)# no shutdown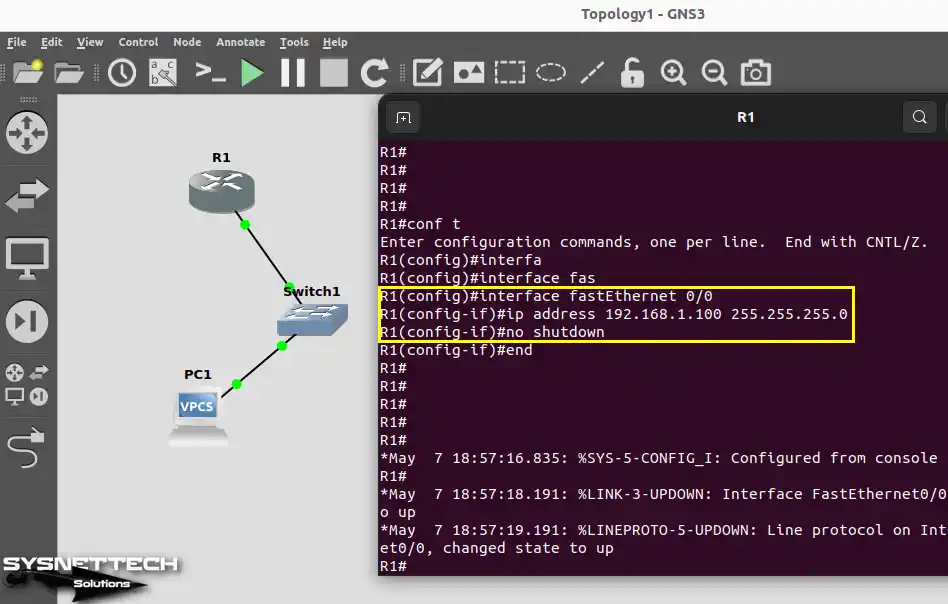
Step 10
Execute the ping 192.168.1.100 command to ping R1 from PC1.
ping 192.168.1.100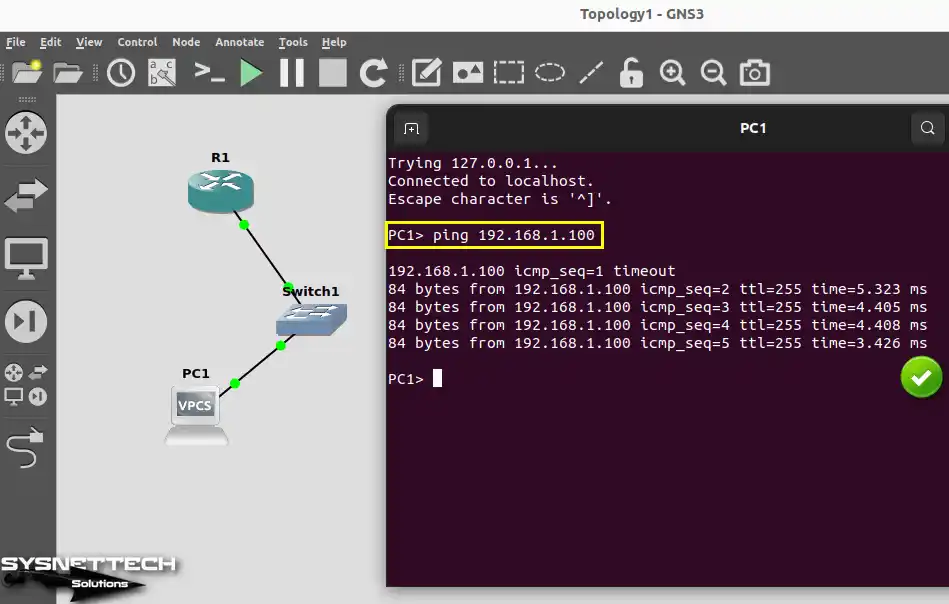
Step 11
To ping PC1 from Router R1, execute the ping 192.168.1.200 command.
ping 192.168.1.200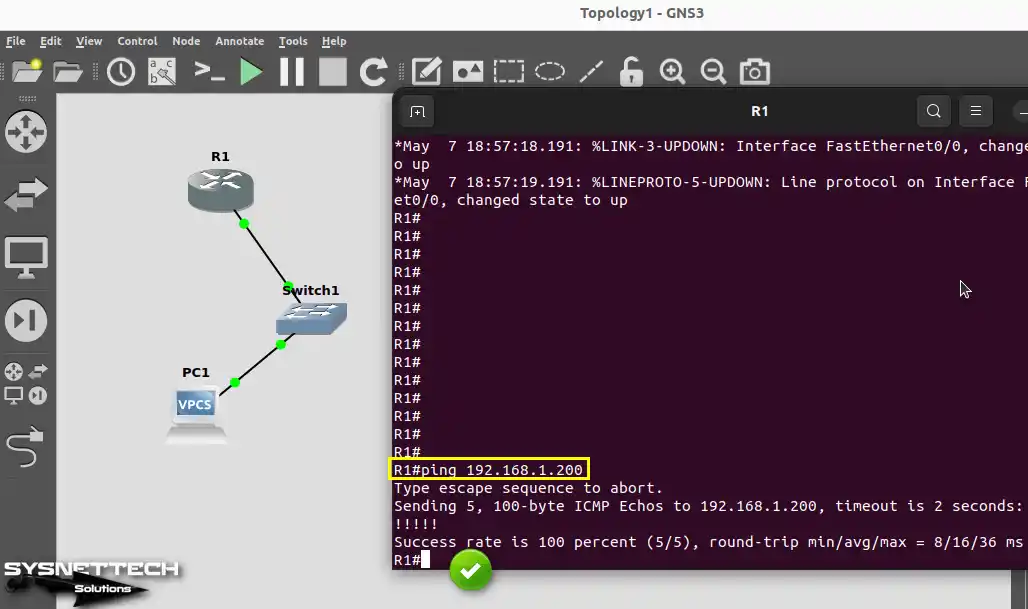
How to Uninstall GNS3 from Ubuntu
Using a single command in the terminal, you can remove or delete the GNS3 network simulator software from your Ubuntu computer.
Step 1
After backing up your network projects, open the terminal and execute the “sudo apt remove gns3-gui gns3-server” command to remove GNS3 from your system entirely.
sudo apt remove gns3-gui gns3-server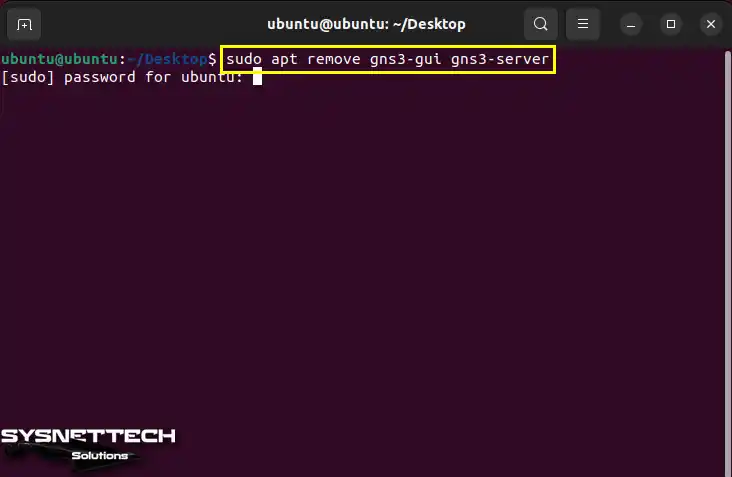
Step 2
Confirm the removal of all dependent packages related to GNS3-GUI and GNS3-SERVER from your system.
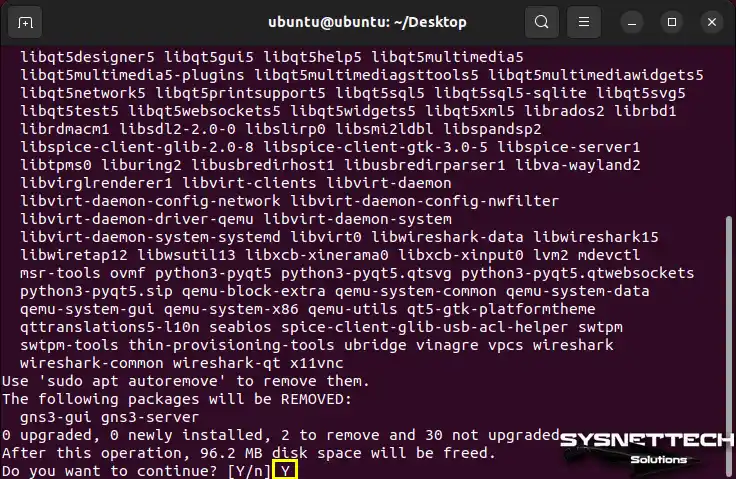
Step 3
After deleting GNS3, execute the “sudo apt autoclean && sudo apt autoremove” command to delete all unnecessary packages and program files on your system.
sudo apt autoclean && sudo apt autoremove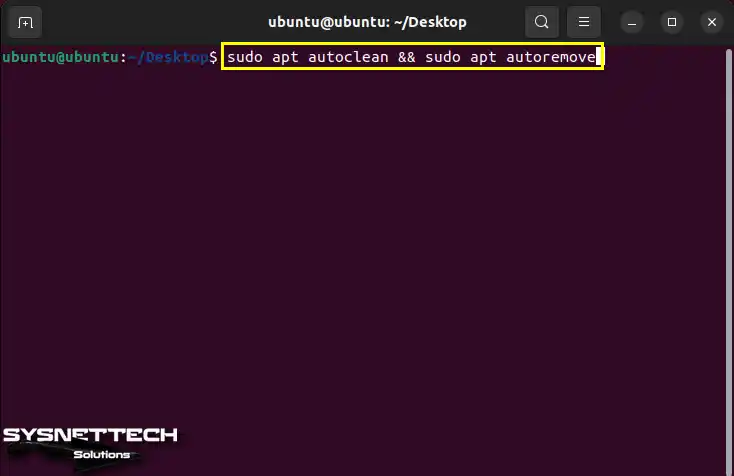
Step 4
After this process, confirm the deletion of unnecessary packages from your system.
Video
Installing Old Versions
| GNS3 | Ubuntu | YouTube Video | Slide |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8.7 | 17.10 | Watch | – |
| 0.8.7 | 18.04 | Watch | – |
| 1.5 | 16.10 | Watch | – |
| 2.0 | 17.04 | Watch | – |
| 2.0 | 17.04 | Watch | – |
| 2.1 | 17.10 | Watch | – |
| 2.1 | 17.10 | Watch | View |
| 2.1 | 18.04 | Watch | View |
| 2.2.17 | 20.10 | Watch | View |
| 2.2.29 | 21.10 | Watch | View |
| 2.2.32 | 22.04 (NEW) | Watch | – |
Conclusion
As a result, by installing GNS3 on your Ubuntu PC, you will get many opportunities for networking expertise. Primarily, you can create a virtual lab and improve yourself better. You can also test complex networks without the need for physical hardware.
In summary, GNS3 enhances your knowledge of networking concepts and allows you to practice your skills. This will prepare you for certification exams and real-world scenarios. As you explore the emulator’s features, you will gain valuable experience for your networking career.

Just thank you !
You’re welcome, thanks for your comment!
thank you i spend a lot to fix dydynamips in *64 ,i couldnt. now its working
I’m glad you fixed the problem. Thanks for your comment.
Could not start Telnet console with command ‘gnome-terminal -t “R1” -e “telnet localhost 5000″‘: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: ‘gnome-terminal’
How to fix this issue, I am running the GNS3 on my Laptop Ubuntu Mate 20.04
Hello. Thanks for the detailed instructions. There is an important question. How to add this Ubuntu to the GNS3 network.
Hello. You can add Ubuntu to the GNS3 environment as a VM, or use the Cloud tool. For example, install Ubuntu in VMware Workstation and after adding Cloud in GNS3, you can select the VMnet you have assigned to Ubuntu from the network adapters and add it to the network.
I’m encountering issues when attempting to integrate virtual machines from VirtualBox and VMware into GNS3 2.2.51 while using Linux Mint 22. The virtual machines are not showing up in the list of available machines to add to projects. Moreover, saved projects vanish upon restarting GNS3, and I’m unable to locate them even when trying to open them from their original save directory.