AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) is called a port because it is a single device developed by Intel Corporation in 1996. It is used to eliminate low performance from graphics cards using the PCI bus, and its design includes PCI 2.1 specifications.
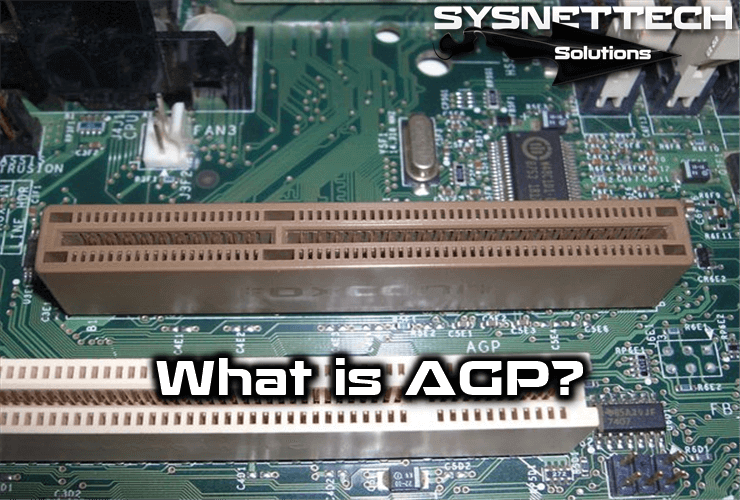
What is the AGP Slot in a Computer?
AGP graphics cards began to appear in 1997 in systems compatible with the x86 architecture of the time.
They needed a chipset based on the Pentium Socket 7 or Slot 1 processors. In addition, Microsoft added support for AGP by releasing Service Release 2 on Windows 95.
This port is 32-bit, similar to PCI, but it has significant differences, such as eight additional access channels to RAM.
In addition to accessing directly over the northbridge, it also manages to emulate video memory in RAM. Also, the bus speed is 66 MHz.
Operating Modes
The accelerated graphics port bus has different operating modes.
1X
The 66 MHz speed has 266 MB/s transfer speed and operates at 3.3V voltage.
2X
It has 133 MHz speed, 532 MB/s transfer speed, and operates at 3.3V voltage.
4X
It has a 266 MHz speed, 1 GB/s transfer speed, and operates at 3.3 or 1.5V voltage to match the graphics card’s designs.
8X
The 533 MHz speed has a transfer rate of 2 GB/s and operates at a voltage of 0.7V or 1.5V.
These transfer rates are achieved by using bus clock cycles but without physically changing them.
This port is used only for the connection of graphics cards, and due to its architecture, there may be only one slot that is approximately 8 cm and is located next to the PCI slots.
Starting in 2006, this slot was no longer used due to the emergence of PCI-Express, which provides more benefits in terms of frequency and bandwidth, and manufacturers of motherboards such as AMD and NVIDIA produce fewer products for this port.
Advantage Between PCI and AGP
The AGP graphics slot has many advantages over PCI-connected graphics cards. AGP is a bus/system specially designed for use in graphics adapters, unlike PCI.
The most significant advantage of this port is that adding a particular channel to the CPU improves performance by providing faster communication and information transfer.
Backward Compatibility
AGP cards were compatible with older equipment, but there were some limitations. Some cards included different types, such as standard and professional versions, which resulted in slot mismatch.
Some cards had voltage compatibility issues, requiring 1.5 volts, and others 3.3 volts.