CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol) operates on all Cisco devices in a network. Its primary function is to discover and identify neighboring devices. Moreover, it facilitates efficient network management and troubleshooting.
What is the CDP Protocol in Cisco Networking?
CDP protocol belongs to Cisco and operates in the data link layer. Cisco devices have this feature enabled by default, which is helpful for administrators. As a result, they can get the network’s topology effectively.
CDP’s default enablement might cause security issues, so consider turning it off. The CLI prompt achieves this using the “no cdp run” command.
Preventing information collection about connected Switches restricts data access. As a result, Switch A avoids gathering data about the other two Switches.
When managing a Cisco network, use CDP to find interface connections. So, you can determine how a particular Switch links to other Switches.
What Does CDP Protocol Do?
CDP is a potent network monitoring tool widely used by administrators. It collects information on Cisco devices that are directly connected to other devices. Moreover, it gathers address information and protocol summaries efficiently.
How Does CDP Work?
Computer networks rely on connected devices, as most cannot function independently. Thus, they connect to devices of the same type or with different functions. Devices create a network, with each having one or more neighbors. So, they establish connectivity and communication within the network.
Upon booting, Cisco devices automatically start this service and discover devices. Additionally, they share hardware and software information directly with connected neighbors. Furthermore, this occurs regardless of the protocol or application of other devices on the network.
Enabled by default on active Cisco devices, this protocol sends periodic messages. At specific intervals, the system sends these messages directly to connected devices.
Messages contain device type, router interfaces, connected interfaces, and model numbers. As a result, they provide essential information about the connected devices.
Obtaining more information about the network design allows the creation of the topology. Thus, administrators can form the physical and logical network design based on collected data.
Devices within the same address range are neighbors; otherwise, they aren’t. Thus, it cannot consider devices in different subsets as neighbors.
Physically connected devices use the Cisco discovery protocol. Hence, it operates at layer 2, enabling communication between them.
What Information Does It Discover?
CDP discovers the following information from network devices and shares it with neighbors:
- Device Identifier: It identifies the hostname assigned to a Cisco Switch or Router.
- Address List: It defines network layer addresses for supported protocols.
- Port Identifier: CDP specifies local and remote port names for interfaces like FastEthernet. Furthermore, it uses ASCII characters for GigabitEthernet interfaces.
- List of Capabilities: It defines whether the devices on the network are a Router or Switch.
- Platform: CDP explains the hardware platform of network devices, including Cisco 7200 routers.
- VLAN: It represents the VTP domain and Native VLAN information.
- Port Status: It describes the duplex status of the port.
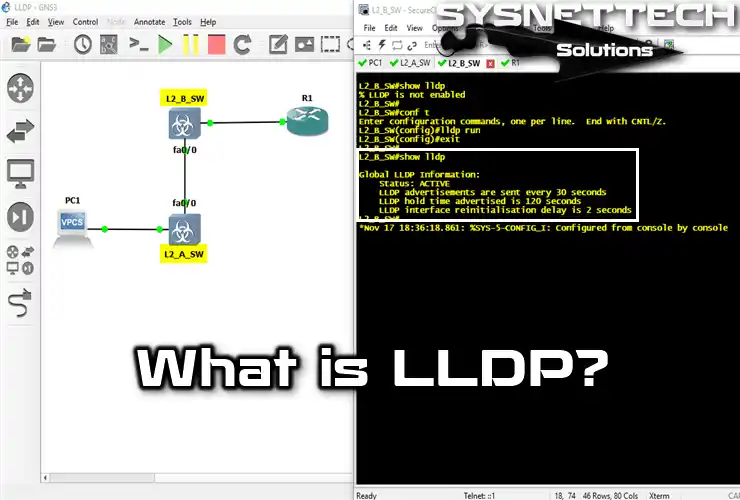
How to Check Neighborhood Information on Cisco Router
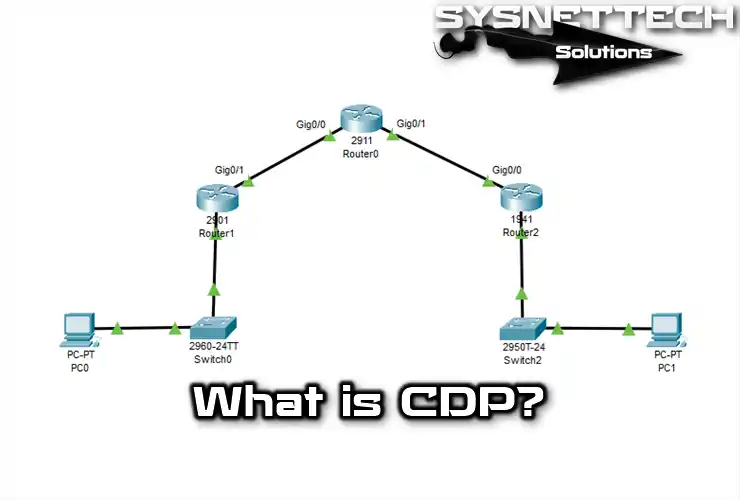
Let’s check the information on devices connected to a Router. For this purpose, we will use the Packet Tracer simulator software and refer to the article’s title image.
1) show cdp neighbors
Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans Bridge, B - Source Route Bridge
S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, P - Phone
Device ID Local Intrfce Holdtme Capability Platform Port ID
Router Gig 0/0 141 R C2900 Gig 0/1
Router Gig 0/1 140 R C1900 Gig 0/0
2) show cdp interface gigabitEthernet 0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Sending C-D-P packets every 60 seconds
Holdtime is 180 seconds
Router#
3) show cdp entry *
Device ID: Router
Entry address(es):
IP address: 192.168.1.2
Platform: cisco C2900, Capabilities: Router
Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0, Port ID (outgoing port): GigabitEthernet0/1
Holdtime: 173
Version :
Cisco IOS Software, C2900 Software (C2900-UNIVERSALK9-M), Version 15.1(4)M4, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc2)
Technical Support: http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Copyright (c) 1986-2012 by Cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Thurs 5-Jan-12 15:41 by pt_team
advertisement version: 2
Duplex: full
---------------------------
Device ID: Router
Entry address(es):
IP address: 192.168.2.2
Platform: cisco C1900, Capabilities: Router
Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1, Port ID (outgoing port): GigabitEthernet0/0
Holdtime: 172
Version :
Cisco IOS Software, C1900 Software (C1900-UNIVERSALK9-M), Version 15.1(4)M4, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc2)
Technical Support: http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Copyright (c) 1986-2012 by Cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Thurs 5-Jan-12 15:41 by pt_team
advertisement version: 2
Duplex: full
Router#
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is Cisco CDP used for?
- Is CDP Layer 2 or Layer 3?
- Why do we need CDP?
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a handy tool for taking care of networks. It helps administrators locate and identify devices that are close by in a Cisco network.
Usually, CDP collects essential information about connected devices. This info includes what type of device it is, the ports on the router it’s connected to, the ports on the device itself, and what model the device is.
But having it on by default might make things less secure. Administrators can make it safer by turning it off. Still, it provides valuable info for managing networks well.