The Hub is a piece of network hardware that allows us to concentrate LAN traffic from multiple computers and rebuild the signal.

What is a Hub in a Computer Network? What are the Differences Between Switch and Hub?
The Hub is a device with a certain number of ports, and its sole purpose is to receive binary data entering one port and send it to other ports.
In this case, a request for a specific PC on the network is sent to all PCs on the LAN. This dramatically reduces bandwidth and causes LAN listening problems.
Hub works as a Repeater at the first level of the OSI model. That is why it is sometimes called a multiport repeater. In short, it is nothing more than a combination of multiple RJ45 sockets.
Hub Types
Hubs are divided into two categories: Active and Passive. In the active category, devices are connected to an electrical power source, and the signal sent to different ports is renewed.
On the other hand, passive category devices send them to all their connected hosts without raising the signal.
Usage
Multiple hubs can be connected to centralize a large number of computers, and this is called a daisy chain.
To do this, you only need to connect devices using a cross cable, that is, a cable that connects the input/output ports on one end to the ports on the other end.
Hubs usually have a unique port called an uplink to connect two hubs using a connecting cable.
Some devices can automatically bypass or unlink ports, depending on whether they are connected to a host or Hub. Daisy can be arranged in up to three centers.
If you want to connect more than one computer to your internet connection, a hub is not enough.
You will need a network manager device or Switch, or as long as other computers on the network want to access the Internet, you will leave the equipment directly connected as a gateway.
Hubs and Switches carry the connection of a LAN, so these devices seem to do the same job, but they do not.
Although terms like Switching Hubs are sometimes used, both words have different meanings. Still, it is necessary to know the Ethernet Protocol to understand the differences and benefits between the Hub and the Switch.
Difference Between Switch and Hub
It basically extends the functionality of the LAN so that the cables can be extended over a longer distance, so this network device can also be considered as a repeater.
The most apparent problem between these devices is that this device transmits Broadcasts to all ports. So, if it contains eight ports, it sends the same information to all the computers connected to it. So, this only sends broadcasts per port.
It can also be considered as an intelligent network device.
When the Switch is started, it usually begins to recognize MAC addresses sent by each port.
In other words, when the information comes to the Switch, it has more information about which output port is the most suitable and, therefore, does not load a load on its other ports.
Ethernet: due to the nature of the broadcast transmission protocol, the use of this device in the local LAN may allow information to be hacked.
When it receives information, it raises serious concerns about security as it sends information to all connected nodes.
Simulation of Ping Between Hub and Switch on Packet Tracer
As you know, Packet Tracer network simulation software is an application developed by Cisco. You can download this software after you register with Netacad, or you can directly access the links from our article.
We prepared and presented a GIF file for you to examine the working principle/logic of an Ethernet Hub device in a network on Packet Tracer.
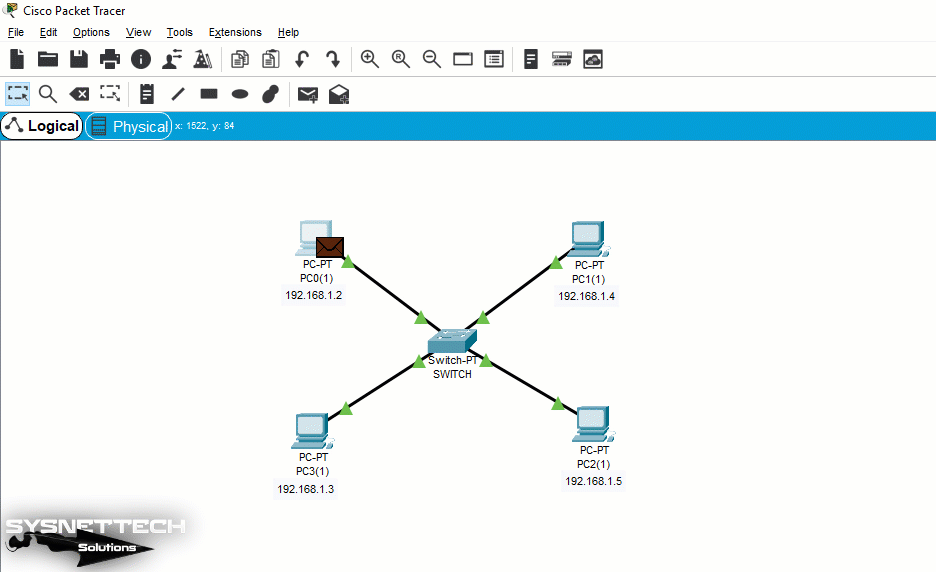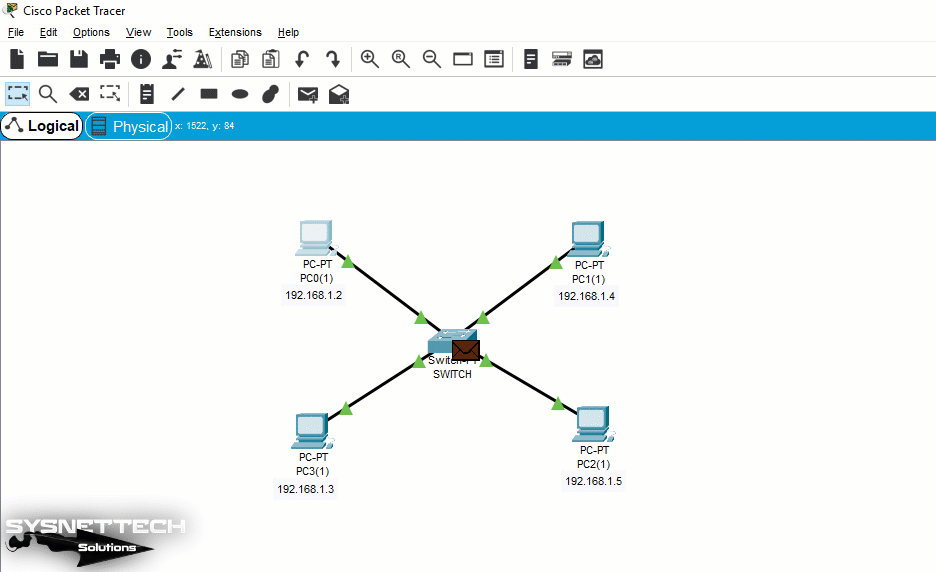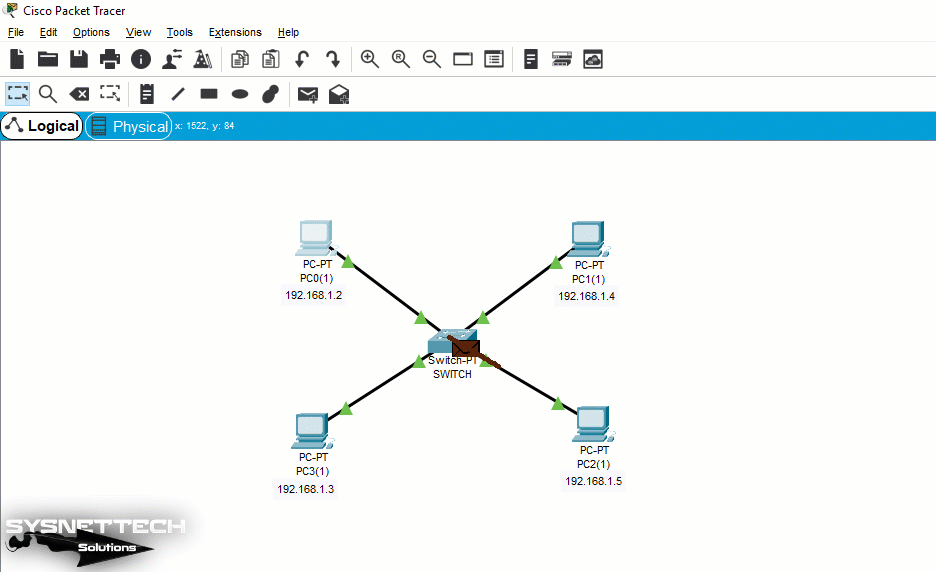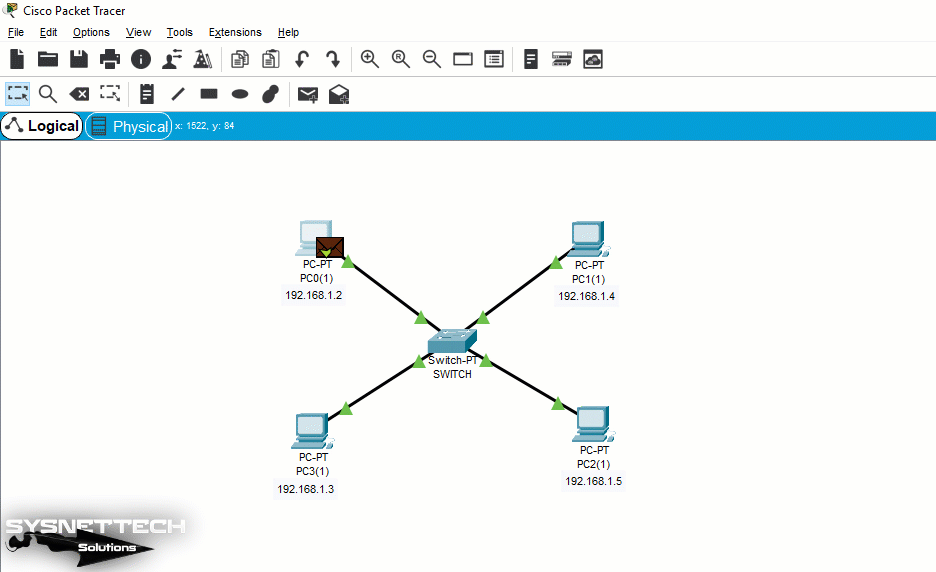
Hub Logic
As you can see in the network below, there is a hub connected to four computers. In this structure, when you ping from PC0 to PC2, you can see the Broadcast storm because ICMP packets are sent to all connected computers. This will cause substantial bandwidth problems in an extensive LAN.
Switch Logic
The GIF file below shows you the working logic of an Ethernet Switch. After analyzing the above reasoning, you can see how much address-oriented data is transferred by a switch.
Here, while pinging from PC0 to PC, ICMP packets are sent by evaluating only the MAC address of PC2 on the Switch.
Conclusion
As a result, it is vital to understand the working logic of Hub and Switch devices for efficient networks. Moreover, hubs are simple and work to transmit data to all devices.
But, of course, switches are more intelligent. That is, it sends data to specific recipients. Ultimately, knowledge about LAN hardware ensures optimum performance and security.