ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is for IP control/error reporting. It generates error messages for service availability and router/host status.
Moreover, ICMP is a sub-protocol used for the control and error reporting of the Internet Protocol (IP). Error messages are like signals that tell us if something is working or not. They can show if a device or connection is not available.
What is the ICMP Protocol, and What Is Its Role In Network Troubleshooting?
User apps do not directly use ICMP protocol on a LAN. It differs from TCP and UDP. However, ICMP is generally not used by user applications on a network and is quite different from how TCP and UDP work.
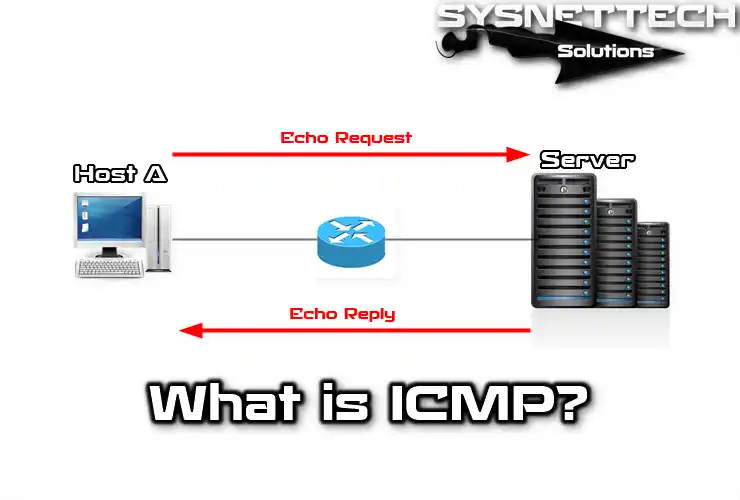
ICMP’s primary purpose is to Ping or Trace LAN computers. It sends Echo ICMP request messages to calculate availability, travel time, and route through computers. In short, it serves Ping and Trace functions, determining LAN PC details.
ICMP is in an IP protocol package (RFC 792). Messages respond to IP errors, diagnostics, and routing. Furthermore, these notices handle IP errors, diagnostics, and routing.
ICMP protocol notices have two basic versions at the network layer. So, these messages come in two basic versions at the layer;
- ICMPv4 for IPv4
- ICMPv6 for IPv6.
The system encapsulates messages with a new IP header and transmits them as datagrams. Consequently, each device has a TTL value for IP packets.
If the TTL value is 0, the source receives a Time Exceeded message. Furthermore, the ICMP protocol packet verifies the connection. Not all ICMP messages ensure packet delivery in the IP datagram. However, some notices contribute to successful packet transmission.
The application typically forwards the error message to review and send. Subsequently, it ensures appropriate message content transmission.
The only benefit of this process is checking whether a packet can reach its destination when its TTL is full.
What Does ICMP Do and How Does It Work?
Generates the ICMP protocol, error & control messages in local networks, aiding troubleshooting. Additionally, it assists in problem detection and correction. Most 3rd party software that controls devices on the web uses ICMP notices.
Users use Ping and Traceroute to identify computer OS issues. Furthermore, these commands help pinpoint specific problems accurately.
Ping checks devices using Echo Request and Reply messages in LANs. Additionally, it controls Time to Live and Destination Unreachable using UDP datagrams.
Traceroute determines routers and hosts between source and target devices. So, it identifies problematic devices along the route. In short, it controls the hop count of the path to the destination and the devices through which the packet goes.
ICMP protocol only reports to system administrators and does not fix errors.
What are ICMP Messages?
1. Echo Request / Echo Reply
It uses echo messages to determine if a device on the network is functioning.
The local computer sends an Echo Request to the target computer. Subsequently, the receiving computer responds with an Echo Reply.
2. Destination Unreachable
Destination Unreachable message informs of unreachable target or service. Thus, it alerts the computer about the unavailability.
The computer sends an Unreachable message for undeliverable packets received. So it notifies the sender of the issue. In this scenario, it generates codes to elucidate the non-transmission of packages.
The codes include;
- Destination Unreachable: 0.
- Network Unreachable: 1.
- Host Unreachable: 2.
- Protocol Unreachable: 3.
Network and Host Unreachable messages are router responses indicating packet transmission failure. Moreover, these notices provide valuable information about the specific cause of the loss.
When a router or server receives a routeless packet, it can reply with a Destination Unreachable message. This response signifies LAN inaccessibility. Furthermore, these responses are pivotal for resolving connectivity problems effectively.
The last router may respond with a message: network known, target inaccessible. Additionally, this response aids in identifying connectivity issues accurately.
3. Time Exceeded
The IP header limits the packet routing through the TTL value. Furthermore, this ensures efficient delivery to the destination.
Without TTL limitation, routers would create endless loops in the network. Furthermore, this ensures efficient packet delivery to the destination.
The TTL value in the IP header restricts the number of routers a packet traverses to reach its target. Moreover, it prevents packets from endlessly circulating within the LAN.
The router sends a Time Exceeded message to the source. Additionally, this indicates packet failure due to expired TTL.
4. Redirect
Routers inform LAN computers of the optimal route through Redirect messages.
The router receives a packet with the route and informs the next hop using the ICMP protocol. So, it redirects the message to the source computer.
5. Source Quench
Source Quench implements flow control, telling the source to pause sending. As a result, it regulates packet transmission temporarily.
The message instructs datagrams to adjust transmission speed based on resource availability. So, it optimizes LAN performance and resource allocation effectively.
Computer reports Source Quench to transport layer, utilizing TCP flow control. Thus, it manages packet flow in LAN communication.
ICMP Information Messages
| 0 | Echo Reply |
|---|---|
| 3 | Destination Unreachable |
| 4 | Source Quench |
| 5 | Redirect |
| 8 | Echo |
| 11 | Time Exceeded |
| 12 | Parameter Problem |
| 13 | Timestamp Request |
| 14 | Timestamp Reply |
| 15 | Information Request |
| 16 | InformationReply |
| 17 | Addressmask Request |
| 18 | Addressmask Reply |
Internet Control Message Protocol Error Messages
| 0 | It cannot reach the network. |
|---|---|
| 1 | It cannot reach the destination host or application. |
| 2 | The destination does not have the requested protocol. |
| 3 | The system cannot reach the destination port, or the target application is not free. |
| 4 | While fragmentation is necessary, the corresponding flag indicates otherwise. |
| 5 | The source path is not correct. |
| 6 | The destination network is not known. |
| 7 | The destination host is unknown. |
| 8 | The source host is in an isolated state. |
| 9 | Administrative reasons prohibit communication with the target network. |
| 10 | Administrative reasons prohibit communication with the target host. |
| 11 | The type of service prevents reaching the destination network. |
| 12 | The type of service prevents the target host from being achieved. |
Conclusion
If I had to explain ICMP, it’s like the messenger of IP communication, sending error & control messages. Thus, it helps you figure out what’s wrong with your LAN setup. For instance, tools like Ping and Traceroute can quickly spot problems on the network.
Generally, the ICMP protocol is super essential for tech-savvy folks like you, especially if you’re an advanced system admin. It’s crucial to understand these messages. That way, you can fix LAN issues and make your digital world more dependable.