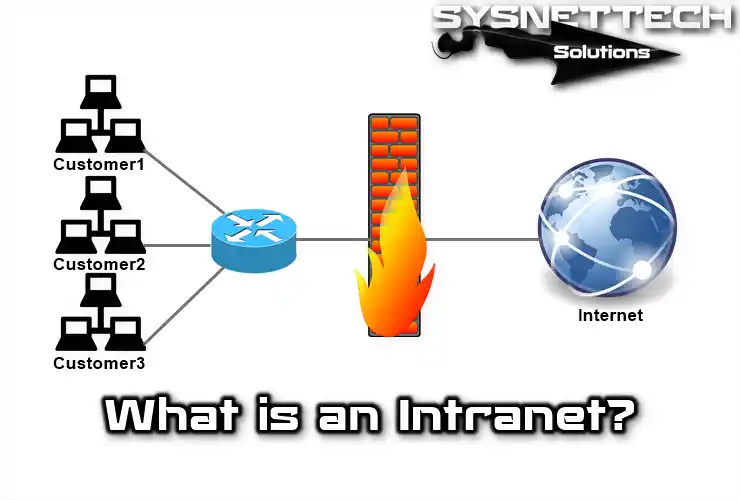
An intranet is a private network using Internet tech. Corporate firms create internal networks with TCP/IP. It works on various hardware for Internet communication. Additionally, people know these networks as intranets.
What is an Intranet Network? What is the Importance of Private or Internal Networks?
The Intranet network needs hardware and software protocols. Thus, it collaborates effectively with local area webs.
Big firms back up databases on central servers while designing the LAN. Also, this actually protects crucial data during web planning.
The Intranet network has a web server for specific services, with security controls. Also, this setup ensures benefits and maintains safety protocols.
Intranet Usage Areas
The Internet is changing how businesses communicate, share info, and advertise. Similarly, it allows people to learn more and do business more efficiently.
Many companies have started using intranets to make it easier for people to talk to each other. Thus, they became trendy because they were easy to use.
Companies without TCP/IP structures miss the Intranet’s uninterrupted benefits. However, an intranet network offers seamless access to information and help.
TCP/IP LANs aid global access at home or traveling. This convenience allows people to connect worldwide effortlessly. An intranet network connection is like a particular Internet for people working in the same company. It helps the company work better.
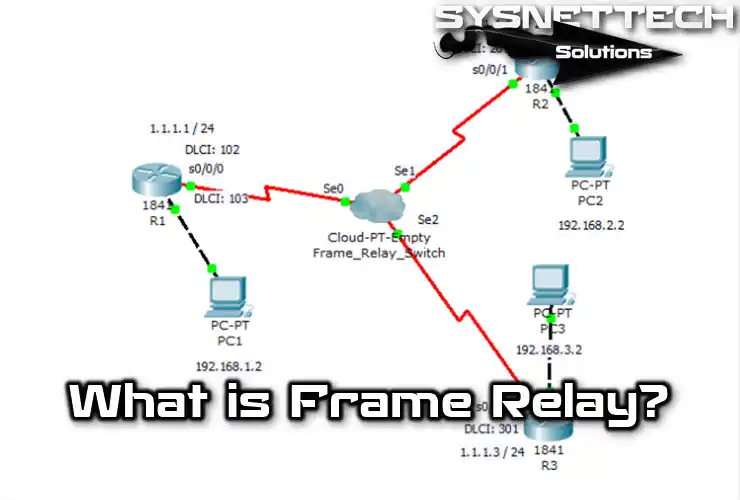
The Intranet differs due to its paramount security systems. Further, these structures differentiate it from the Internet. A firewall protects the company’s LAN and limits access to specific targets. So, it defends the LAN and manages authorized resources.
Collaboration’s key: intranets support shared apps. This enhances productivity and teamwork in companies. Also, task jobs aid by secure idea exchange. Hence, this method improves efficiency and results.
Free software enables Internet services, increasing the value of networks for companies. Thus, LANs that have value for companies have grown even more.
Features of Intranet
An intranet is a private network for businesses and schools using TCP/IP protocols. Also, it transmits data within organizations’ boundaries.
Protocols work with net hardware; they’re compatible with IPX. Also, they match various devices and standards effectively.
Network users access online resources; the Intranet is accessible with proper settings. So, an Intranet requires specific locations to access the web.
The Intranet connects networks within the company via TCP/IP protocol. As a result, diverse LANs collaborate within a company’s Intranet. Subnets refer to different LANs within PCs. So, they create an organized structure within the design.
Special software lets people work together and send emails on a private network. It also helps them talk and work as a team in their company.
Software Used in Intranet
Apps send info, aid projects, and manage finances within companies. Also, these apps are exclusive to each specific company. Apps written in tools like JavaScript and C++ enhance net functions. In this way, these programming tools strengthen application development on networks.
Standard software like Internet Explorer, Chrome, and Microsoft Office aids functions. Also, these programs ease regular tasks on the net.
Networks enable industry trades like orders and payments between businesses. So, they ease smooth processes and economic relations among firms. There is no online need for transactions between Intranet areas. Likewise, they work independently without requiring an internet connection.
A firm can have a home user order a product online by configuring the Intranet network to do business online. When you order online, the system securely sends your info. Then, the company’s internal LAN processes and completes the order.
Order info sent online reaches its destination through routers. These routers examine the IP address in each TCP packet and forward it to the next router. If the router is nearby, it sends packets directly. Otherwise, it finds a suitable route to send them.
For different LANs, packets pass through Internet-connected routers. In this way, routers manage data flow to various webs.
Firewall guards data and limits Intranet network access to authorized users. In this way, sensitive info remains secure from unauthorized access.
Web Services in Intranet Network
WWW enables Intranet creation and sharing of web resources across areas. Moreover, it allows accessible and secure resource sharing within the company via HTTP or HTTPS protocols.
It allows web pages with multimedia content: text, graphics, audio, and video. In this way, diverse elements combine to create engaging web content.
HTTP accesses resources; access the internal network via a web page. Moreover, this enables efficient connectivity to company designs.
Services rely on client-server structure, local client software, and servers on the Intranet. So, these configurations ensure effective communication and resource sharing.
As a result, such services are realized based on client and server relationships. Client software runs on a local personal computer, while server software runs on a hosted Intranet. The thing to note here is that client software goes beyond specific operating systems. Furthermore, it’s versatile across various types of systems.
High-speed cables in intranets create efficient LAN connections. As a result, data traffic flows quickly via these lines.
Network Growth and Subnets
Large intranets need effort to manage as a single network. Furthermore, handling them as a unified system involves dedication. The LAN is divided into subnets for better management and organization. In this way, each section becomes more manageable and efficient.
Even though a company can have different locations, they are all connected in one extensive LAN. This aids collaboration; routers access remote subnets. Thus, they enhance contact and teamwork among areas. As a result, they enable communication between different network parts.
For corporate subnets, use specific IP addresses assigned by Internic Registry Services. So, these addresses are essential for configuring segments.
Private networks: A, B, C classes. A for larger, C for smaller ones. Additionally, the Class A LAN supports 127 networks and 16,777,214 nodes.
Class B networks can consist of 16,383 LANs and 65,383 nodes. Class C LAN can consist of 2,097,151 LANs and 254 nodes.
As intranets grow, finding ways to manage information flow between different places becomes essential. This is especially true when dealing with locations that are far apart.
For efficiency, create a second network in the remote branch office. This setup manages data more effectively across different PCs.
Intranet and Network Security
Intranet networks face attacks; malicious individuals can damage or steal data. So, security measures are crucial to safeguard valuable info.
Internet breaches can expose businesses to malicious attacks. Thus, ensuring protocol security is essential for protection.
To keep everyone safe, we use a combination of hardware and software to manage traffic. This is important for security and helps create a secure environment for everyone.
Encrypt for authentication, virus scans, and blocking unwanted sites. So, these steps enhance shield and web efficiency.
Firewall: guards, allows certain, blocks bad; proxy server strengthens security. Similarly, proxy servers enhance network protection and control.
The proxy server watches traffic entering and leaving the network, which aids security. Further, it assists administrators in managing and securing LAN activity.
Use strict authentication for network security in corporations; it’s vital. Likewise, these measures ensure only authorized access to the LAN.
The server blocks unwanted sites, enhancing user online safety. So, this software restricts access to undesirable web addresses. Combined with server antivirus software, it ensures virus-free files. So, this approach guarantees a safe background.
A router should filter out inappropriate people or insufficient data that cannot reach the network. The router inspects packets, IP, and header; the admin controls entry. Besides, only authorized personnel manage the router’s usage.
Site-blocking software examines URLs from Internet requests. It checks each URL against a database of unwanted sites.
The blocking software prevents access when it detects objectionable URLs. Thus, it ensures that such info doesn’t pass through the network. In this case, it checks URLs for inappropriate words and provides secure browsing.
As a result, it guarantees a safer online experience. With the Internet expanding, updating the list of dangerous websites is essential.
Conclusion
To summarize, the simple answer to the question of what an intranet network is or why we use it is that it facilitates uninterrupted internal communication. In addition to improving cooperation, especially between companies, it also ensures the security of sensitive data.
Moreover, they support wide-ranging projects through services such as the web and special software. In short, advances in PC networks, such as intranets, undoubtedly continue to deliver business efficiency in the corporate arena.