RTCP, an essential thing called Real-Time Transport Control Protocol, helps people talk on the Internet. It ensures it’s safe when we send stuff online; nobody can snoop on it.
Also, it works well with RTP, which makes things like talking on the web, having video calls, and playing games online much better.
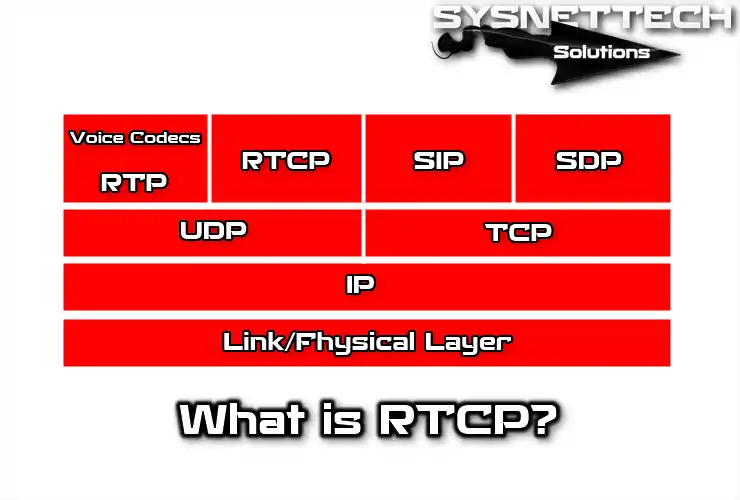
What is RTCP Protocol in Networking?
RTCP does the job of sending packets like RTP does. During this process, it uses the transportation system and regularly shares control data with all participants in the session.
However, it uses a different link point than RTP and usually relies on consecutive sources in a stream.
RTCP’s feedback is responsible for sharing info about the quality of the data. When it uses data, the performance of the app gets better. Also, it adjusts the encoding to reduce the bit rate.
The identification system is a consistent task at the transport layer for RTP sources. Moreover, it skillfully brings together different parts, making sure everyone’s sound and video work together perfectly.
It regularly sends participants feedback and descriptions in packets during the session. Later, they control the speed of sending these packets to allow more participants to join.
Participants look at the numbers of each one because they send control packets to all other participants. They calculate the sending speed of control packets using this number.
It’s a protocol that allows basic info about the participants of a session and the quality of service to be conveyed in an RTP stream.
RTCP History
The development of audio and video transmission tech, which dates back to the early days of the Internet, connects to the history of RTCP.
So, to enable real-time data transmission, the IETF introduced RTCP in 1996 with RFC 1889. This file has the protocol’s simple working, plus data gathering and sharing.
Back in the ’90s, folks craved instant online audio and video. Internet lacked real-time data then; it was essential. That’s why developers created the RTP and RTCP protocols.
Over time, they improved it even more, and as a result, they presented the RFC 3550 document. This file improved how we do things: it gives us more options, makes it work smoother, and performs much better.
Today, considering the Internet is a basic human need, we can understand how vital protocols such as RTCP are in web platforms.
What are the Features of Real-Time Protocol?
Let’s check out the essential aspects of the Real-Time Transport Control Protocol.
- Control and Monitoring
As you can understand from its function, it enables controlled data transmission in real-time streams and keeps track of it. At the same time, it ensures the secure exchange of info between two parties. In a few words, the primary purpose is to improve the quality of online meetings.
- Gathering Statistics
Real-time protocol collects statistics like delay times, loss rates, or bandwidth during data streaming. Collected, inherently valuable data is vital for network admin and software devs.
- Reporting Data
Comparing statistics data, they also make some reports about data quality. In this manner, developers can improve their apps by utilizing these reports.
- Timers
Real-time protocol checks the flow at specific intervals through timers to keep the connection quality as high as possible. This way, it prevents and takes precautions against potential link issues.
- Package Structure
The RTCP packet that completes the data collection and reporting job contains info and statistics about traffic flow.
- Flexibility
It’s flexible because it works well with different apps. This way, it runs smoothly with other real-time software.
- Updates and Standards
IETF regularly updates the Real-Time transport protocol. That’s why it stays up to date because it changes based on advancing tech and needs.
Basic Working Principle
Each packet starts with a fixed section, like RTP data packets. Also, it contains variable-length items structured based on the packet type.
This protocol first checks the statistics for receiving data packets (SR/RR) based on bandwidth during its job. Then, it sends packets when it achieves the highest speed.
New receivers in the session understand the source from a CNAME value source. They check the number of packet types in the first packet to determine the process.
Also, the real-time protocol calculates the packet transmission interval to allow for thousands of participants, from one or two. For this, it uses the session’s bandwidth in each one when calculating among the participants.
So, the bandwidth must be as much as the network’s capacity, and the app that initiates the session must provide the speed value.
RTCP and RTP Relationship
RTCP and RTP cooperate to transmit audio, video, and other data over the web in real time. The difference between these two protocols is this:
- RTP: It packages, transmits, and receives real-time info. In short, it manages the basic process of transferring data.
- RTCP: It splits packets during data exchange. It adds timestamps, sequence numbers, and error correction info to each package.
In simple terms, RTCP controls certain aspects, while RTP acts like a delivery person who carries and delivers packets to their target. That’s why these protocols complement each other.
Real-Time Transport Protocol’s Packet Structure
There are five different types of packets for the kind of data provided in a session:
- SR (Sender Report)
Includes transmission and reception statistics for participants who are active senders.
- RR (Receiver Report)
Includes reception statistics for participants who are receivers but not active senders in a session.
- SDES (Source Description)
This protocol describes various pieces of info such as the source name, email, phone number, etc.
- BYE
Allows a station to indicate the end of its participation in a session.
- APP
It is a particular signal packet specific to the app.
The real-time transport protocol makes the number of members in a session for RTP stream control. This way, it calculates the SR or RR information range by making evaluations.
After all, as the number of members increases, each of them is granted access to the session based on the state of the network. So, if two people are in a voice session, it will send packets every 5 seconds. If it is for a four-person session, it sends packets every 10 seconds. In this case, the most frequently sent RTCP packets are SR and RR.
RTCP Advantages and Disadvantages
Now, let’s examine some of the pros and cons of RTCP in data transfer:
Pros
- Ensures Quality in Data Flow
It monitors and controls the quality of info in instant data streams. It will make the presentation much better and will make the people who are attending the session enjoy it even more. Thus, it avoids possible delays or packet losses.
- Detects Problems and Fixes Error
Collecting info about the link during a session identifies and fixes errors. As a result, it enhances the stability of live sessions.
- Provides Convenience in Network Management
RTCP carefully gathers session data, giving network administrators and software developers a lot of helpful information. In this way, we can see RTCP’s essential traits. So, it eases network management and development tasks.
Cons
- Consumes Bandwidth
The real-time transport protocol sends data back and forth during a session, which can strain the bandwidth. That’s why a high speed is needed for good conversation quality. But, people with slow internet speeds may experience quality issues.
- Needs Additional Power
It checks the traffic to keep the session active. Thus, it requires more hardware resources.
- Configuration Difficult
To make RTCP work effectively, you must go through many detailed processes. That’s why configuring it takes more time.
Uses of Real-Time Transport Protocol
The uses of the RTCP protocol can vary based on personal needs. Yet, its most common purposes are:
- VoIP (Voice over IP) and Video Conferencing Applications
RTCP is most prominent in VoIP and video conferencing apps. In this way, all members connected to the web can have real-time conversations with each other.
- WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication)
Users use WebRTC from web browsers to achieve purposes like voice and video calls, file sharing, or screen sharing.
- IP and Telephone Exchanges
They use RTCP to maximize voice quality in IP and PBX-based phone systems.
- Gaming Applications
They use this protocol to optimize bandwidth in online PC games.
- IP Cameras and Security Systems
In security systems, IP cameras must process images in real-time. This is why they employ this norm to enhance live video quality.
- Telemedicine Applications
In medicine, RTCP helps doctors see patients from far away. This means doctors and kids can talk easily and have an excellent time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About RTCP
- What do they use the RTCP protocol for?
- What is the difference between RTP and RTCP?
- What is RTCP for streaming?
- What is the difference between RTSP and RTCP?
- Can RTP work without RTCP?